Email Us :
info@labcompanion.cn-
-

Requesting a Call :
+86 18688888286
Are Tantalum Capacitors Resistant to "Coldness or Heat"? --Let's Find the Answer from Dragon Temperature Forcing System--Froilabo

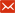
With the continuous innovation and progress of mobile communication technology, human society has entered the information age. With the rapid development of the information age, all kinds of electronic smart devices and communication equipment are constantly innovating, bringing convenience to people's lives. In many electronic and communication products, each component plays a vital role in the use of the product. Among them, tantalum capacitors are small in size but can achieve large capacitance, because of the excellent performance, they are not only widely used in military communications, aerospace and other fields, but also in industrial control, film and television equipment, communication instruments and other products. In addition, due to the weak voltage and current resistance of tantalum capacitors, the three common failure modes are mainly voltage type, current type and heat type, and it is easy to cause burst combustion after failure. Therefore, tantalum capacitors need to be subjected to failure analysis before application. In order to investigate the influence of ambient temperature change on tantalum capacitors, dragon temperature forcing system--Froilabo is undoubtedly the best choice. It can test and certify tantalum capacitors according to the "ESCC inrush current Tantalum capacitor" standard.
Dragon temperature forcing system--Froilabo
Dragon temperature forcing system--Froilabo is capable of rapid heating and cooling to simulate the extreme temperature environment and thermal shock to components. Dragon uses air cooling temperature control mode, which can be used for ultra-long continuous temperature control from -72 ° C to +225 ° C. As shown in Figure 1 below, dragon temperature forcing system--Froilabo is testing the capacitor, installing the capacitor on the electronic device, passing the steady output of direct current, and generating small noise (ripple) at the output end, the test purpose is to verify that the capacitor can operate normally under extreme temperatures.
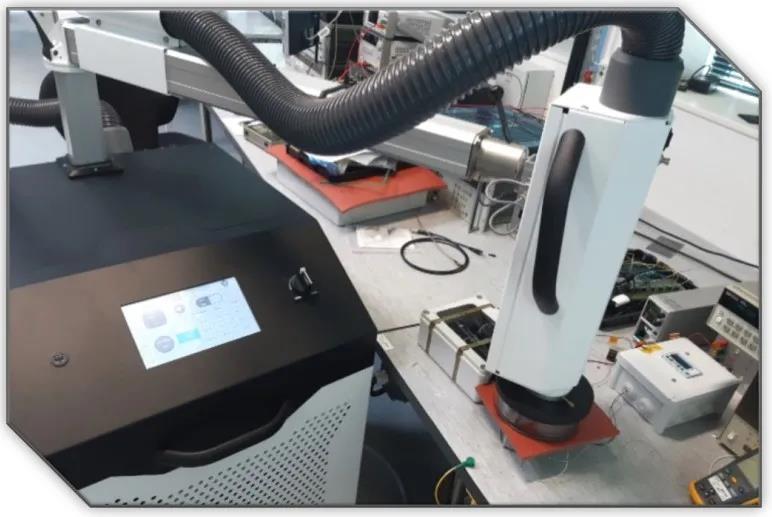

FIG. 1 Tantalum capacitor test - new dragon temperature forcing system--Froilabo
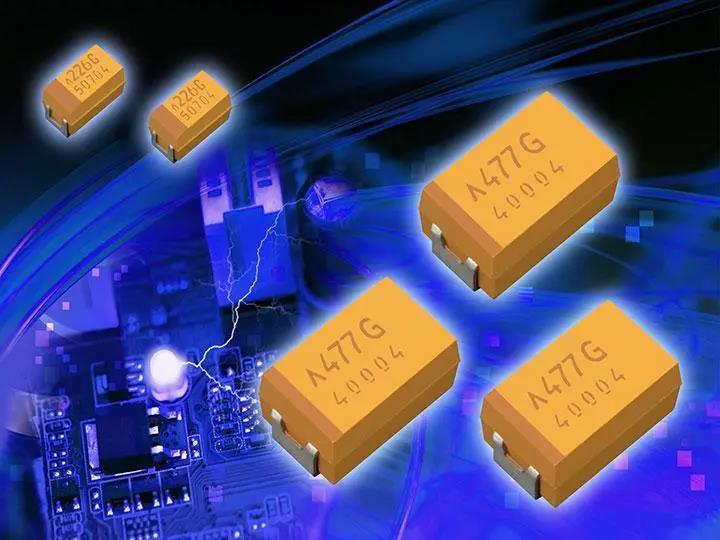
Typically, the test condition is to charge and discharge the capacitor for 10 cycles between -55 ° C and +85 ° C (the limit test temperature can be adjusted to +125 ° C or +200 ° C, which can be adjusted for different applications). The schematic diagram of the circuit switch of the electronic component is shown in Figure 2 below. When the mechanical switch 1 is closed, a certain voltage is applied to the capacitor, and the circuit is regarded as a short circuit, so the current value is large; When the capacitor is in the charging state and the current value is almost zero; When switch 2 is closed, the circuit voltage is 0V, at which time the capacitor is in a discharge state until the current is almost zero.
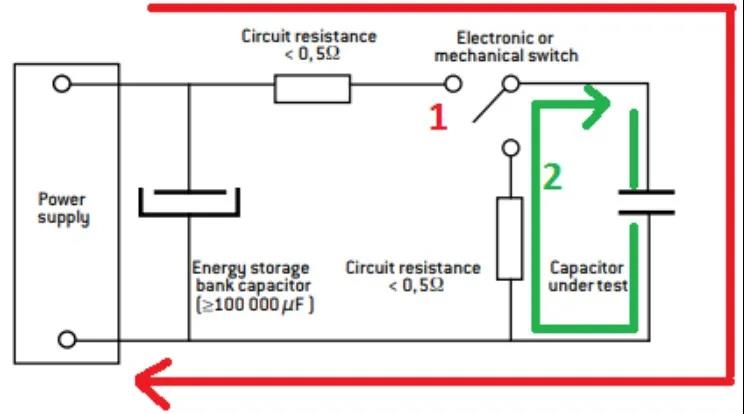
FIG. 2 Electronic components in inspection
 FIG. 3 Tantalum capacitor under test
FIG. 3 Tantalum capacitor under test
After 10 cycles of charging and discharging, the leakage current of each capacitor is measured to investigate the influence of temperature change on it.
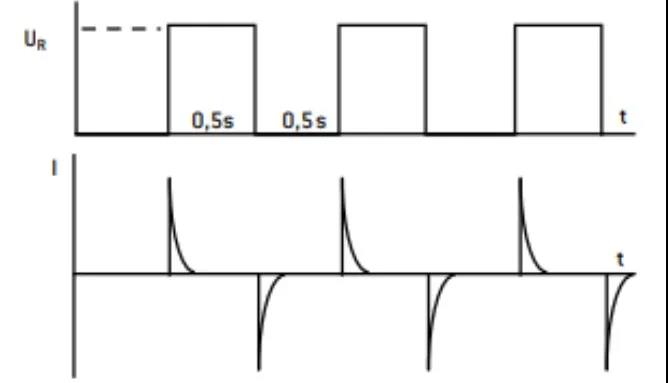
FIG. 4 Leakage current detection of tantalum capacitors
Figure 4 shows the remaining current (I) passing through the capacitor when it is fully charged to its rated current (Ur), monitored within 5 minutes of each charge in µA. The leakage current is equivalent to the insulation resistance of a capacitor, so it must be as low as possible. The leakage current value is a function of the capacitance value and the resistance value. Figure 5 below records the change of the leakage current value with temperature.
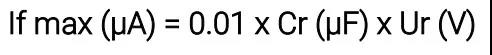
(20℃时)
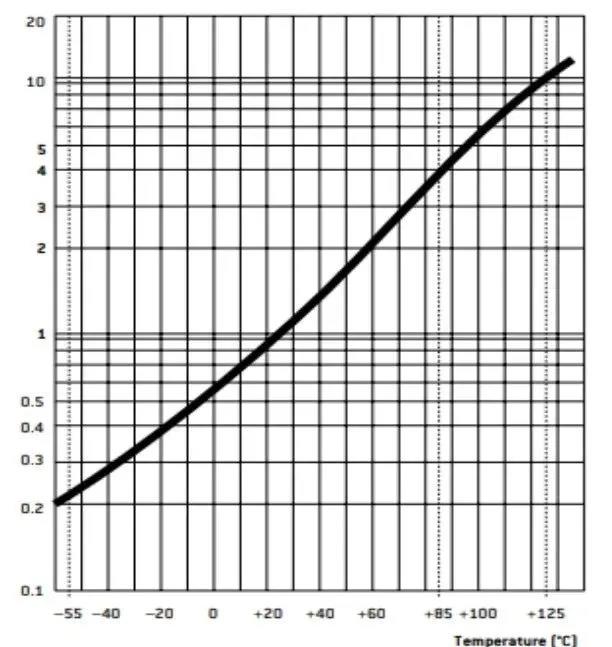
FIG. 5 Relation of leakage current value with temperature variation
As shown in FIG. 6 and FIG. 7 below, the capacitor whose leakage current value is almost zero in a short time can pass the failure analysis test; The capacitor whose leakage current value fluctuates with the change of external temperature is regarded as a failure component, and it is easy to cause burst combustion after failure.
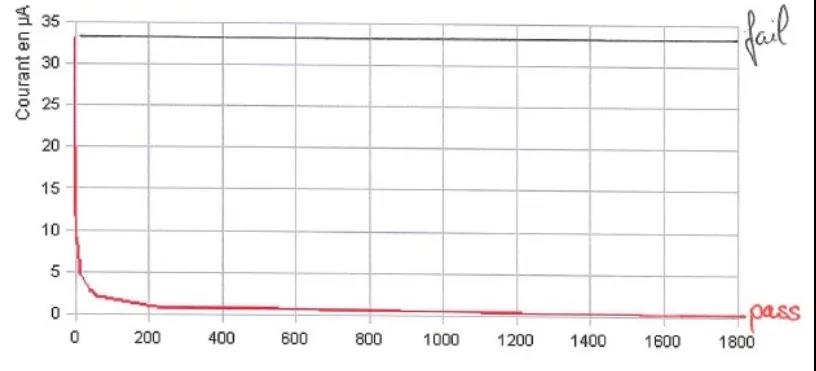
FIG. 6 Change of leakage current of capacitor with time
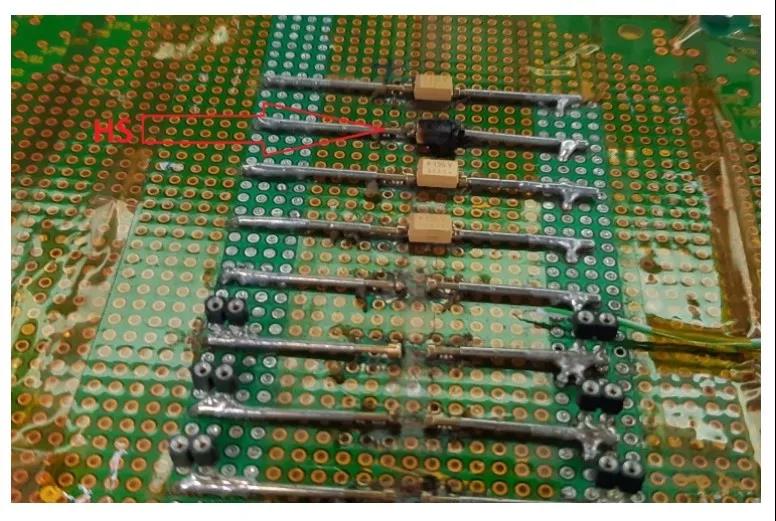
FIG. 7 Failure analysis test of tantalum capacitors